Photoshop 7.0
WorkArea
What you can see in Photoshop User Interface?
Initial Photoshop environment has the following components:
- Title bar
- Menu bar
- Options bar
- Tools palette
- Other palettes
Controlling Palette
show/hide all palettes: Tab
show/hide all palettes except tools: Shift+Tab
All the palettes can be managed with Window Menu
Open an existing image
File–>Open (Ctrl+O)
(or)
Open required folder contains pictures–>Drag the picture into photoshop area
Each image will be opened in its own window. Many Images can be opened at a time but one can be activated.
Manage Opened Images
change between opened images: ctrl+Tab
Close current Image Window: Ctrl+W
Check the size of already saved image: Image menuàImage Size
Create duplicate of opened image: Image Menu–>Duplicate
Adjusting Work Area
Usually designers use keyboard shortcuts and hot keys to complete their work fast. Some times the opened palettes appear clumsy. You can more work space by simply focus on one image without any distractions. This can be possible through Full Screen mode option.
There are three options to work with the current image into full screen
Standard
FullScreen with Menu bar but no title bar
FullScreen without Menu bar and title bar
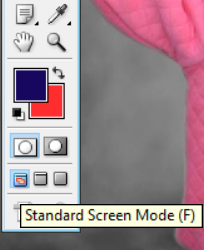
The options available at the bottom of the Tools palette. You can also change between these modes by simply pressing ‘F’
Changing Magnification level of image
view image in fit in window: Ctrl+0
view image in actual size(100%): Ctrl+Alt+0
Magnifier and Hand tools are located at the bottom of the tools palette. Magnifier is used to bring the desired portion of the image to close and also to reduce the magnification. Hand tool is used to move the image across the screen to see the remaining portion of the image when it is in magnified.
magnify image from its center: Ctrl+ +
decrease magnification from center: ctrl+ –
change to zoom in tool temporarily: hold Ctrl+space and click/drag
Change to zoom out tool temporarily: hold alt+space and click
Change to Hand tool temporarily: Hold Space and drag
TYPES OF TOOLS
All the tools of Photoshop are available in the tools palette usually appear at the left side of the screen. Each tool provides some functionality.
Some hidden tools in tools palette can be recognised by a small arrow at bottorm right corner of a tool. Hidden tool can be disclosed by holding down mouse pointer for a while or hold shift while using its respective KBS.
There are 4 categories of tools in PS:
- Selection Tools: These tools are used to select some portion or entire image.
- Marquee tools: (KBS: M) used to select from image in basic shapes.
- Rectangular marquee
- Elliptical Marquee
- Single Row Marquee
- Single Column Marquee
- Move tool(V): used to move/copy the selected part to within the image or into other image.
- Lasso Tool (L): used to select portion of the image in freeform style.
- Magic Wand (W): used to select portion of the image based on similar color.
- Crop Tool (C): used to terminate unwanted portion from the image.
- Slice tool (K): used to create Hyperlinks in Web Designing.
- Painting tools: used to paint some color on image.
- Brush/pencil(B): used to paint foreground color in different shapes and styles
- History/Art History brush (Y): used to paint color based on states and snapshots in History Palette
- Gradient/Paint Bucket Tool (G): Gradient is used to fill a bunch of colors in the selected style while Paint Bucket is used to fill a single color or pattern
- Dodge/Burn/Sponge Tools (O): Dodge is used to lighten the color in the image, Burn is used to darken the color while Sponge is used to remove or enhance the color
- Blur/Sharpen/Smudge Tools (R): Blur tool is used to soften the color, Sharpen is used to harden the color and Smudge is used to create finger painting effect.
- Eraser/Magic Eraser/Background Eraser (E): Eraser tool erases the color while dragging the mouse, Magic Eraser erases the color based on color similarity while Background Eraser intelligently removes the color from the complex or uncleared areas.
- Clone/Pattern Stamp (S): Clone stamp used to create duplicated portion while pattern stamp used to paint with a pattern.
- Healing/Patch Tool (J): Healing brush used to repair the imperfections in the image in painting style while Patch tool used to correct them in replacing style.
- Shape Tools: used to create basic or custom shapes
- Type tool: used to create text objects. Horizontal, Vertical, Horizontal Type Mask and Vertical Type Mask are varieties of type tools.
- Shape tools: used to draw basic or custom shapes
- Pen tool: used to create custom shapes with paths and curves. Freeform pen, Add anchor point, delete anchor point, Convert point are different tools available under Pen.
- Direct/Path selection tools: Both are useful to edit the path while creating shapes.
- View tools: used to change the view of the image or work area
- Annotation tool: used to provide text or audio annotation
- Eye Dropper tool: used to pick a color from the opened image.
- Hand tool: used to move the image like moving a paper on the desk.
- Magnifier: used to increase or decrease magnification of the image view.
CREATING NEW IMAGE
Default name of a file in the Photoshop is Image. Every file is simply an image for the photoshop. No second page can be inserted in the same file like text-based apps.
New image in Photoshop can be created using: FileàNew (Ctrl+N)
Options in the New Image Dialog:
Size: The physical dimensions of the image should be mentioned here. Either we can choose from the predefined sizes or enter dimensions manually. Page sizes to be selected based on our final output.
Photoshop is used in different fields like Web Designing, Video Editing, Graphics other than Desktop Publishing.
Resolution: Computer generated graphics can be two types:
- Raster/Bitmap graphics
- Vector Graphics
Raster Vs Vector Graphics:
- Raster graphics are made up of pixels. Vector graphics are made up of mathematical functions representing relationship between elements and paths connecting them.
- Raster Graphics lose their quality when magnified but vector Graphics don’t.
- Raster Graphics requires more memory space than Vector Graphics
Drawing tools can create vector graphics only.
Ex: Tools in Ms-Word, Powerpoint, Corel Draw, AutoCAD
Painting tools can create raster graphics.
Ex: Tools in Photoshop, Corel Photo-paint, FireWorks
In Photoshop we can create Raster as well as vector graphics and can convert vector graphics into raster graphics.
Pixel stands for Picture Element which is a small unit of image. Each pixel can display a color which can have values for Red,Green and Blue. Values for each Red,Green or Blue aspects of color can have 0 to 255.
Resolution is the number of pixels in the image. Resolution determines the quality of image. It depends upon the number of columns and rows by which the image display is divided. More resolution increases the memory requirement of the image.
Color Mode: The mechanism by which the color at the pixel is representing is known as color mode. There are RGB, CMYK, GrayScale, Lab color modes.
Select RGB if you are designing for screen output or select CMYK for printing purpose.
Content: used to specify the initial content of your newly created image. There are 3 options are available:
- White
- Background color
- Transparent
Changing background color can be done by clicking on the background color swatch.
MARQUEE TOOLS
Marquee Tools (Keyboard Shortcut : M): Useful to select a part of an image in a predefined shape. 4 marquee tools :
- rectangular : makes rectangular or square shape selections
- Elliptical : makes elliptical or circle shape selections
- single row : selects single row of pixels
- Single column : select single column of pixels
Selection with Marquee Tools:
- Drag diagonally to specify size of selection.
- Hold down shift to constrain the shape of selection
- moving selection:
- Hold space to change position of selection while selecting.
- If selection was completed, place cursor inside selection and drag
Feather: used to specify the number of pixels at the edges of selection to be blurred. The value of feather should be appropriate to the selection size.
Applying feather:
- Enter the value of feather in option bar, if you want to apply it for the next selection
- If selection was already completed,
- right click on selectionàfeather
- (or) press ctrl+alt+D
Apply transform: Ctrl+T
Cancel last action: ctrl+Z
Cancel last 20 actions (History): ctrl+alt+Z
Anti-aliased: makes the edges of elliptical or circular shaped selections smooth by minimizing zigzag or staircase effect.
Style of selection:
- normal: to select manually
- fixed aspect ratio : to select by maintaining specified aspect ratio
- fixed size: to select in the specified size.
MOVE TOOL (KBS: V)
Move tool is used to move/copy selected part to another or within image.
Select Inverse: Ctrl+shift+I
Deselect a Selection: Ctrl+D
Creating new image based on selection size:
- Make selection
- Copy with Ctrl+C then press ctrl+N
- Paste with Ctrl+V
Photoshop image can be saved in different picture formats. .psd is the default format in which the image will be stored in working state so that it can be modified later. Other formats like .jpg does not allow the image to be modified.
File menuàSave/Save As
TRANSFORMING AND LASSO TOOLS
Transform means changing the form.
Apply Transform:
Edit menu–>Free Transform (Ctrl+T)
In transform mode we can see:
- bounding box
- resize handles
- proxy/base/reference point
upon the selected image.
Options in the options bar while transforming:
- proxy points
- screen coordinates of selected proxy point
- dimensions of the selected image
- Rotate
- Horizontal skew
- Vertical skew
- Apply and Cancel buttons
With transforming we can:
- move
- resize
- rotate
- skew
- distort
- perspective
- Flip
To come out from transform with saving:
press commit button on option bar
(or ) press ctrl+Enter (alphanumeric keypad)
(or) press Enter (numeric keypad)
To come out from transform without saving:
press cancel button on option bar
(or) press Esc key
To apply transformation to selection:
Select menu–>Transform selection
(or) alt+s+t
Lasso: used to make free hand selections. It can’t be used for large area selections as it is required to hold down mouse key continuously until the selection was completed. (KBS: L). Generally used to modify the selections.
Using Lasso Tool:
- click to start selection on the image
- Hold mouse button and move along the edges of required selection
- Release mouse button to finish
- Hold Alt to change to Polygonal Lasso anytime
Polygon Lasso (KBS: Shift+L): used to make polygon shape selections.
Using Polygonal Lasso:
- Click in the image to set the starting point
- Continue clicking along the edges of your desired selection
- Hold Alt if you want free hand selection somewhere
- Use Del/Backspace to remove previous line segments
- Connect the starting and end points to finish selection. (or) Double click or Ctrl+click to finish
Magnetic Lasso (KBS: Shift+L): it traces and creates the selection points automatically while you are moving the mouse pointer around the part to be selected.
Using Magnetic Lasso:
- Click in the image to set the starting point
- Move pointer along the edges of your desired selection
- Hold Alt if you want free hand selection somewhere
- Use Del/Backspace to remove previous line segments
- If the selected point is wrong, you can manually click
- Connect the starting and end points to finish selection. (or) Double click or Ctrl+click to finish
Magnetic Lasso traces points based on some options selected.
Options of Magnetic Lasso:
Width: specify the area from which point to be selected. Set caps lock on to change between actual/precision mode. Use ] or [ keys to increase/decrease lasso width
Edge Contrast: values from 1% to 100%. Set higher value if edges of selection are very clear from background. Set lower value to select low contrast edges
Frequency: values from 0 to 100. Higher the value picks the points quickly.
Pen pressure: option useful only when working with Tab
Magic Wand (KBS: W): used to select pixels in the image having similar color values of the pixel upon which clicked.
Using Magic Wand:
- Click once in the image to select
- Options of Magic Wand:
- Tolerance: values 0 to 255. Lower value selects pixels very similar, higher value increases range of colors to be selected.
- Contiguous: selects only adjacent pixels when checked. Otherwise, selects pixels from anywhere in the image
- Use All Layers: specifies whether to select from current layer or all layers in the image
Desaturate an image: Ctrl+Shift+U (or) Image menuàAdjustmentsàDesaturate
Open Hue/Saturation dialog box:
Ctrl+U (or) Image menuàAdjustmentsàHue/Saturation
Adjust Brightness/Contrast: Image Menuà Brightness/Contrast
SELECTING COLORS
There are two color swatches can be seen at the bottom of tools palette that allow us to select some working color.
There are two types of colors:
- Foreground color: painting color usually apply with the painting tools like brush, paint bucket etc.
- Background color: eraser/paper color usually apply with the eraser tool.
Using Color Picker to select foreground/background color:
- Double click on foreground/background swatches in tools
- color picker dialog appears
- Vertical slider holds the values for the option that has been selected in the radio buttons at right.
- The Big rectangular area is used to adjust the value representing by vertical slider
Selecting a color numerically:
- HSB: Hue (00 to 3600), Saturation (0 to 100%) and Brightness (0 to 100%)
- RGB: Red (0 to 255), Green (0 to 255) and Blue (0 to 255)
- L*a*b:Luminosity(0 to 100), a (Green to Red)( -127 to 128), b (Blue to Yellow) (-127 to 128)
- CMYK: Cyan (0 to 100%), Magenta (0 to 100%), Yellow (0 to 100%) and Black (0 to 100%)
- Hexadecimal value: Color code in Hexa Decimal system (contains only 0 to 9, A to F). color code for black: 000000; color code for white: FFFFFF
exchange fore/background colors: X
change fore/background colors to default: D
SHAPES WITH SELECTION TOOLS
Photoshop selection tools are different than any other painting software. A selection in the Photoshop image is treated independent from its selected part. This strange behavior enables us to create new shapes and do more things like controlling painting tools, filters.
Selection can be moved, transformed independent of its selected part. In other words, we can do more things with the same selection. A selection can also be done even in the transparent background.
Selections can be extended or condensed with the help of selection modifiers.
Selection Modifiers:
- Add to Selection: Adds to the existing selection (KBS: Hold Shift while selecting)
- Subtract from Selection: Removes from the selection (KBS: Hold Alt)
- Intersect with selection: keeps the intersected part of existing and current selections (KBS: hold Shift+Alt)
Fill foreground color to selection: alt+backspace
Fill background color to selection: ctrl+backspace
Open fill dialog box: shift+backspace (or) shift+F5
Apply stroke for the selection outline: Edit menuàstroke
Fill from History – alt+ctrl+backspace
